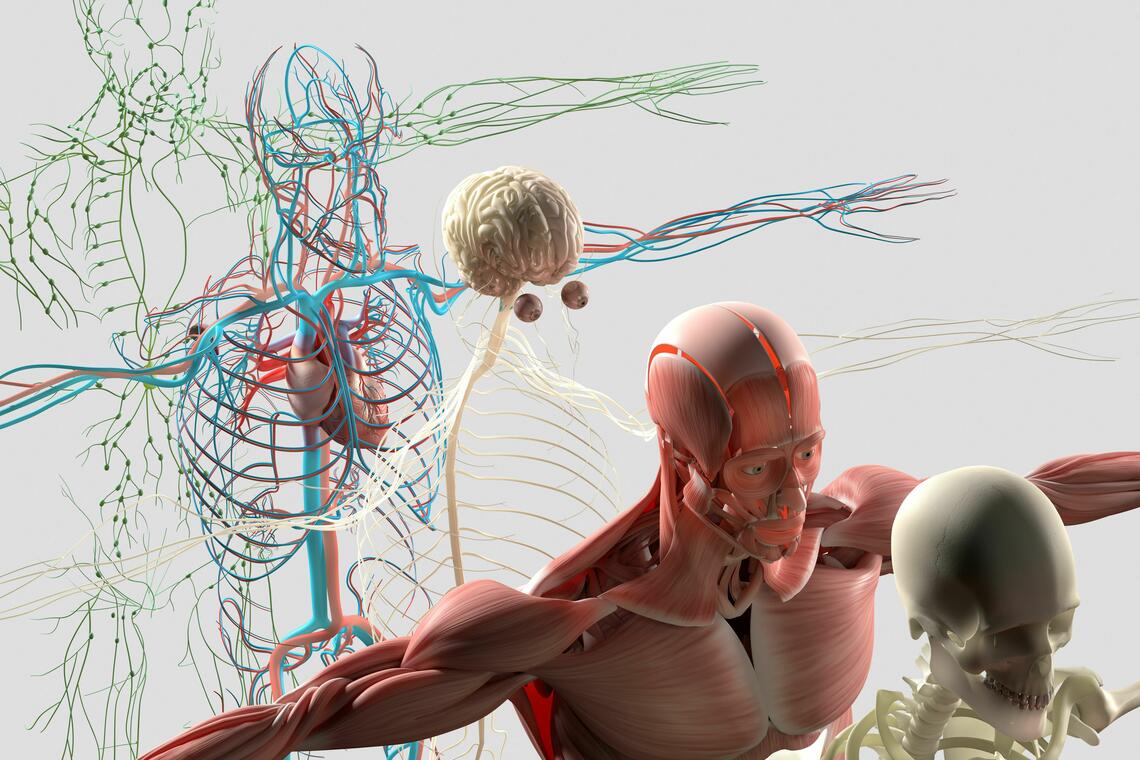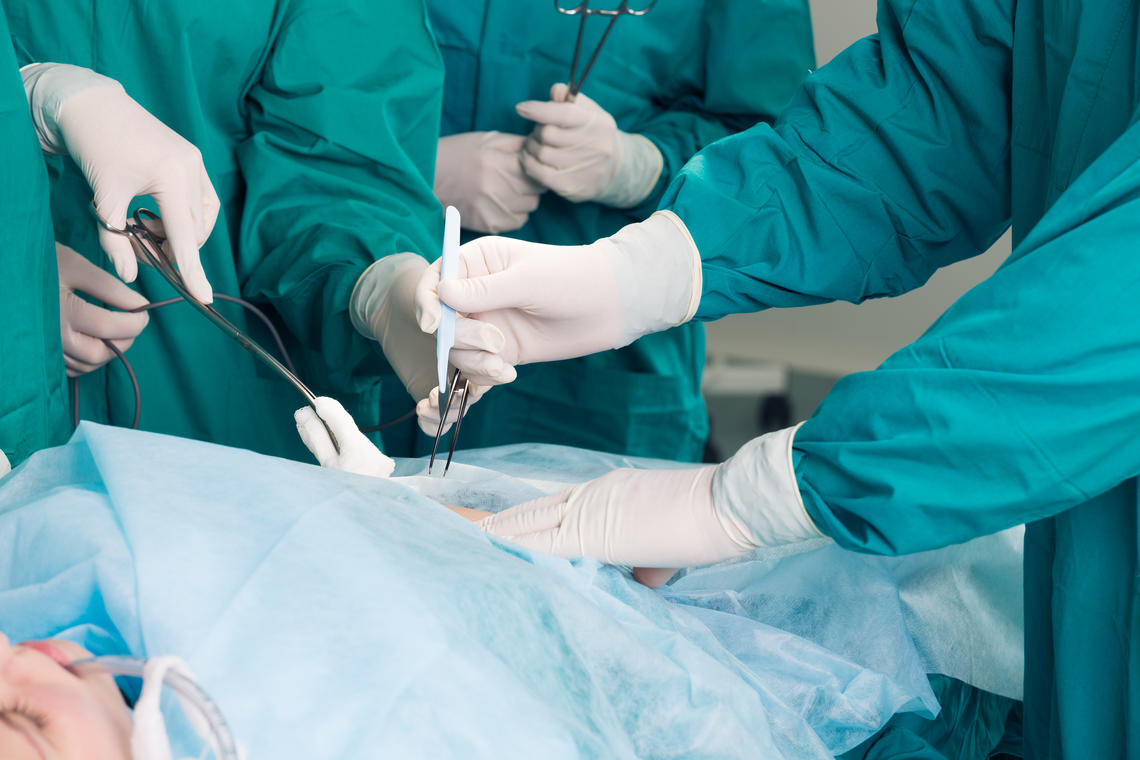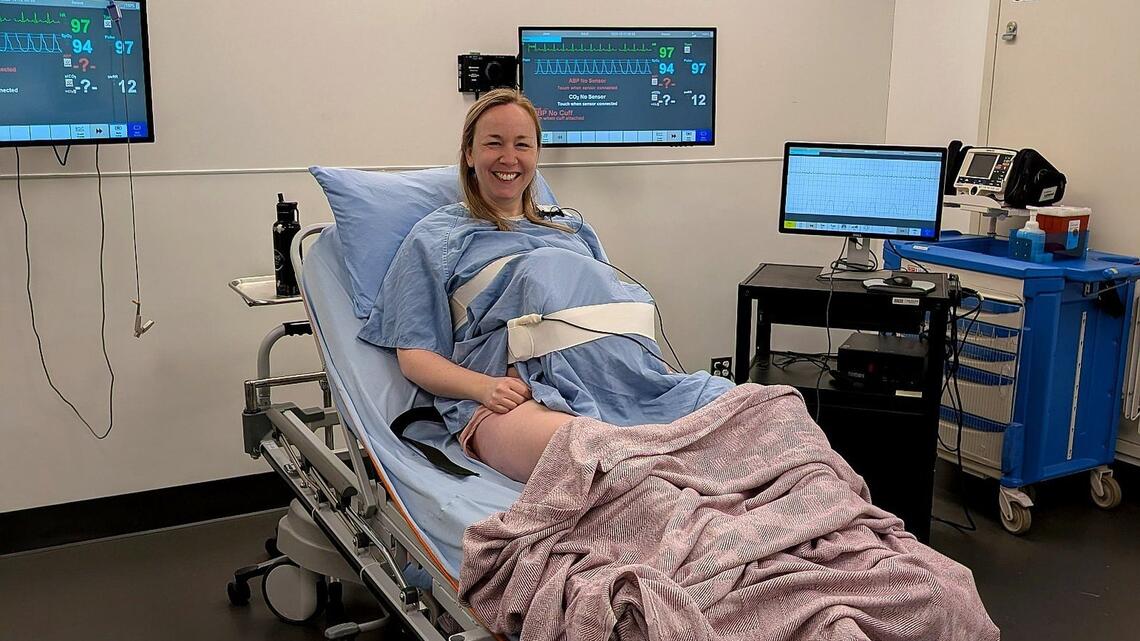
Standardized Patients (SPs) are an essential part of clinical skills training in the CSL. They are trained individuals who simulate real patient scenarios, allowing learners to practice medical history-taking, physical examinations, and communication skills in a realistic, controlled environment.
SPs provide immediate feedback on the learner's performance, helping them refine their bedside manner, diagnostic abilities, and patient interaction techniques.
By simulating a wide range of medical conditions and situations, SPs enable learners to develop essential clinical and interpersonal skills before encountering real patients in a clinical setting.

- Task Trainers: These are specialized models used to practice specific clinical skills such as suturing, IV insertion, and airway management, allowing learners to develop precision and technique.
- Computerized Manikins: High-fidelity manikins simulate real-life patient conditions, including heartbeats, breathing, and vital signs, providing learners with the opportunity to manage complex medical scenarios and emergencies.
- Synthetic Models: These models replicate anatomical structures, enabling learners to practice procedures like joint injections, wound care, and other hands-on medical techniques in a realistic, yet controlled setting.

The CSL features a versatile layout that supports a range of training needs:
- Large Modular Space: This area can be divided into six separate pods, each accommodating 12 learners, providing flexibility for multiple groups to train simultaneously.
- Debriefing Rooms: Private rooms designed for post-simulation discussions, where learners can receive feedback and reflect on their performance.
- Dedicated Simulation Suites with Control Rooms: These suites offer a realistic clinical environment for simulations, with control rooms for facilitators to manage and monitor training scenarios in real time.
Laboratory Activities
If your program involves the following approaches or activities, then the Clinical Skills Laboratory (CSL) is the appropriate space to book.
CSL employs various tools and techniques—such as task trainers, synthetic models, and standardized patients—to create an immersive, hands-on learning environment for simulation-based medical education.
Each of these components serves a unique purpose in helping healthcare professionals develop, practice, and refine essential clinical skills.
-
Standardized Patient
- Role of SPs: Standardized Patients (SPs) are trained individuals who simulate medical cases in a consistent manner, helping students and professionals assess and practice clinical skills.
- Key in Education: SPs play a crucial role in medical education and examinations at institutions like the University of Calgary, offering real-time interaction and feedback.
- Valued Resource: Unlike static instructional materials, SPs provide dynamic, real-world scenarios for training students in medicine, nursing, and other healthcare-related fields.
-
Computerized Manikins
- High-fidelity simulation tools: SimMan 3G and Noelle are advanced computerized manikins used in clinical training.
- Realistic scenarios: These manikins replicate physiological responses, including vital signs, making simulation as close to real-life as possible.
- Diverse training opportunities: SimMan 3G supports various medical procedures and emergency scenarios, while Noelle focuses on labor and delivery simulations.
- Real-time feedback: Students receive immediate feedback on their performance, enhancing learning and skill development in a controlled environment.
- Confidence-building: By providing hands-on practice, these manikins help learners gain the competence needed for real-world clinical care.
-
General medical education curriculum
Focuses on a broad range of fundamental clinical skills required by healthcare professionals across various specialties.
Geared toward training for scenarios encountered in primary care, emergency settings, and general patient care.
-
Teamwork Training
At the CSL, we incorporate a modified TeamSTEPPS framework into our simulation programs to enhance communication and teamwork among healthcare professionals. This evidence-based approach prepares teams for high-pressure clinical settings, improving patient safety and efficiency. Our lab fosters a collaborative environment, equipping professionals with the skills needed for effective multidisciplinary teamwork.
- Hands-on application: Participants practice critical decision-making and coordination, gaining confidence to handle real-life clinical challenges.
- Continuous improvement: Regular simulation sessions help teams identify areas for growth and refine their approach to delivering safe, effective patient care.
-
TeamSTEPPS Components
- Leadership: Cultivating strong team leaders who can guide effective decision-making and ensure clear role delegation during critical medical procedures.
- Communication: Enhancing clarity, accuracy, and timeliness of information exchange to avoid misunderstandings and errors.
- Situation Monitoring: Training team members to maintain awareness of their surroundings and patient status to quickly recognize changes and intervene appropriately.
- Mutual Support: Building a culture where team members provide constructive feedback, assistance, and backup when needed.
-
Training
- Accredited Simulation Training: Our Facilitator Education Training in Simulation course (FACETS) equips educators with skills to design and lead simulation-based learning for postgraduate medical education (PGME) and continuing professional development (CPD) programs.
- Simulation Expertise: Simulation Consultants provide a strong foundation in medical education theory to enhance simulation practices.
- Theory-Based Education: The FACETS course focuses on delivering impactful, evidence-based simulations that are tailored to improve learner outcomes. The KidSIM ASSET and Royal College SET theory, are key components of FACETS,
To learn more about our Simulation Training, please visit:
-
Research
- Research Collaboration: The CSL fosters research to innovate and improve simulation training, enhancing healthcare education.
- Commitment to Excellence: We support ongoing professional development and drive advancements in simulation-based medical education.
To learn more about our research process, please visit: