Analytic Services
The Centre for Health Informatics offers a wide array of analytic services to help researchers elevate their impact and further their research programs. All analytic services can include analytic plan development, ethics application support, and manuscript support for the writing of methods and result sections, if required.
Methods & Analytic Services
We offer various analytic services to help researchers elevate their impact and further their research programs. We can help you develop an analytic plan, apply for ethics, facilitate access to health data, or provide quotes for analytic services and a letter of support for grant submissions. We can meet with you at any stage of your research, the earlier the better however! We would love to help you shape your methods and data plans.
All analytic services can include analytic plan development, ethics application support, and manuscript support for writing methods and result sections, if required, on top of innovative analysis. Our multi-disciplinary team includes analysts with vast skill sets who are ready to work on your project. All projects involved our overarching expertise in epidemiology and biostatistics, some of the others areas we specialize in are: data-related areas including administrative (secondary) data, Electronic Medical Records, and unique datasets or methods-related areas such as natural language processing, machine learning and creating visualization tools.

Data Skills
We have vast expertise in working with administrative health data. This is data that was not collected for research purposes and can often be messy or incomplete. We work to improve data quality while using our skills to use this data to improve healthcare through research and clinical decision tools.
Our team has extensive knowledge on working with Electronic Medical Records (EMR) and extracting data from these records. This process can be complicated but EMR data extraction is a vital skill in health informatics.
We have extensive experience working with unique data created for various reasons such as registry data. This data can be linked with other data sets to create a robust dataset for research in a specialized area.
Methods & Analytic Skills
- Plan, conduct, and report on biostatistical and epidemiological analyses
- Design administrative health data requests
- Design analysis plans
- Conduct epidemiological analyses such as incidence, prevalence
- Conduct biostatistical analyses including modelling
- Create tables and figures that are ready for publication
- Support writing methods and results sections as required and appropriate
Always open for a challenge!
We are happy to support data and analysis needs that are beyond this list.
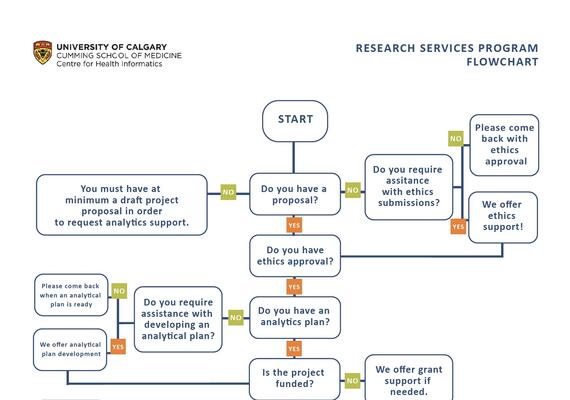
Get Started! Request Services
Meet the CHI Research Services Team
Jessie Hart Szostakiwskyj
Triage Lead
Dr. Adam D’Souza
Senior Data Scientist - AHS Analyst
Rachel Nguyen
Biostatistician
Danielle A. Southern
Senior Research Associate
Fengjuan (Tina) Yang
Biostatistian - AHS Analyst
Brian Steele
Cord Lethebe
Zhaoyu (Mani) Liu
Biostatistician
